Hogar » How to Reduce Cellulite? How Does Cellulite Occur?


Cellulite, or the dimpled appearance of subcutaneous fat, affects approximately 80–90% of post-pubescent women. Although what causes cellulite is primarily a physiological phenomenon, it has become pathologized and points to a moral failing to keep the body beautiful. Interestingly, cellulite and the desire to treat it have received limited empirical attention. Its prevalence and wide acceptance suggest that it is unsurprising and inevitable, yet cellulite treatment is the source of a multi-billion-dollar beauty industry. Such discourse warrants greater psychological attention; poor body image and low self-esteem are correlated. There are many misconceptions about the etiology and maintenance of cellulite, ranging from its association with obesity to localized vascular disturbances. In order to address widespread perceptions and poor sociological discourses of cellulite causes, the present paper provides evidence-based literature on the physiological causes, best treatments for cellulite, and preventable measures of what causes cellulite to better disseminate knowledge to the public, as the educational domain becomes ever more important. Out of a variety of sessions on dermatology and aesthetic medicine, a survey of attendees of the Anti-Aging Medicine World Conference on the hottest concepts in medi-spa treatments revealed that a significant percentage of practitioners were considering or planning to perform best treatments for cellulite. Consumers spend billions of dollars each year in an attempt to rid their bodies of cellulite, attending numerous treatments and procedures in hopes of removing something deemed unnatural, unhealthy, and aesthetically unpleasing. Cellulite, however, is none of these things. The gradient physiological condition, cellulite is simply an evolved state. After this paper provides a background on cellulite, its known causes, possible treatments for a cellulite reduction tips of its appearance, as well as preventative measures, it will then spend time discussing the physiological aspects of cellulite in an effort to foster a more understanding view of this normal and non-debilitating process within the human body.
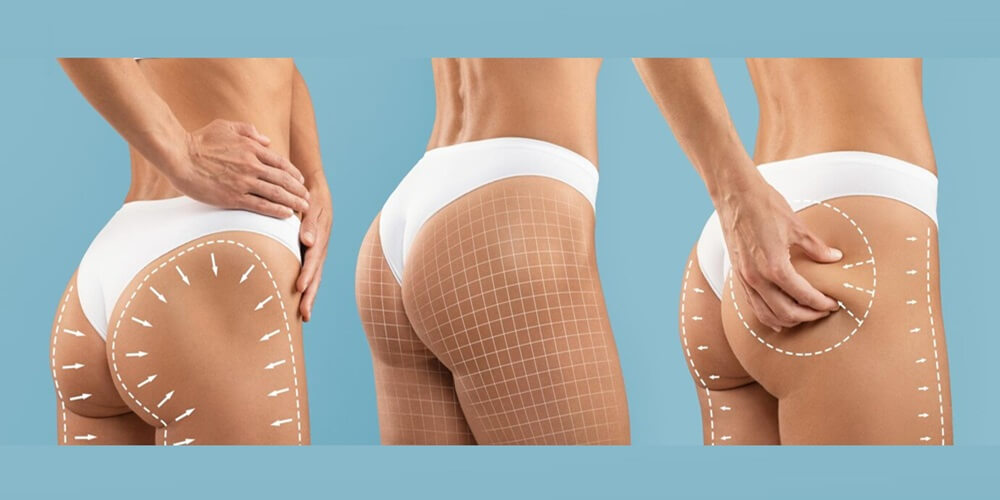
Adolescent females are more likely than men or postmenopausal women to have cellulite causes. Cellulite is physiologically and histologically described as subcutaneous fat surrounded by a fibrous connective tissue matrix arranged perpendicular to the skin surface. Pressure and tethering of the skin cause the fat lobules to bulge upward and protrude irregularly into the dermis, which interferes with venous and lymphatic drainage. Adipocytes, or fat-storing cells, are affected by both hypertrophy and hyperplasia. Diminished dermal and epidermal skin thickness in cellulite-affected areas accentuates the cones and valleys appearance. The rippling and dimpling of what causes cellulite can be made worse by local factors like low skin elasticity, sun damage, and weight gain, but these are not the cause of the condition itself.
Numerous factors contribute to the appearance of cellulite on a macroscopic level. Women are more likely to develop cellulite as opposed to men. Hormones, particularly estrogen and prolactin, contribute to the condition and influence fat storage. Aging decreases skin elasticity and collagen, contributing to more pronounced cellulite causes. Genetics also influence the likelihood of developing cellulite. Weight and lifestyle factors contribute to the condition. The underlying extracellular matrix of collagen and elastin fibers is encased in the subcutis or subcutaneous tissue. The punch-strain test is used to evaluate skin attributes, including dermal stiffness, dermal thickness, and elasticity. Fibroblasts can regenerate skin and secrete collagen and elastin. New insights lead to the core understanding what causes cellulite is formed in the hypodermis, a multi-functional layer between the cutis and muscles; it also acts to connect these layers, reduce forces applied to the skin, and store fat for energy. Consequently, future investigations must shift their focus towards the hypodermis to better understand cellulite causes in order to treat it.
Lifestyle contributes to the build-up of adipose tissue. A diet packed with fruits and vegetables, low in fats, carbohydrates, and salt, does work. Fruits like melons, oranges, pears, and watermelons cleanse the body. Leafy green vegetables like spinach and kale are also fibrous but really filling and low in calories. Other great sources of fiber are in broccoli, cauliflower, and sunflower seeds. Lean and healthy sources of proteins—sea and lean poultry—must replace the fatty meats. Salmon and other fish contain omega-3 fatty acids, which help to keep skin and connective tissue healthy. Too much alcohol will make the skin weak, which then makes the bloating of organs look more pronounced.
It aids the body in exercising, perspiring, and raising the heart rate. Aerobic exercise melts the fat, thus it gives a better appearance. More firm muscle reduces the look of cellulite. Exercising on a routine or regular basis helps how to reduce cellulite. Poor water retention/circulation could be a cause for cellulite. These two problems can be associated with the toxic build-up in the fat tissues called the adipose tissue. The more of this toxin one has, the more cellulites can be. Drinking enough water promotes lean body mass to appear thus less cellulite. For every pound of body weight intake ½ oz. of water. Eliminating bad habits such as smoking will provide some level of benefit to support the skin. Outlets to cope with stress are important in the recovery process. This could be meditation, yoga, and other activities.

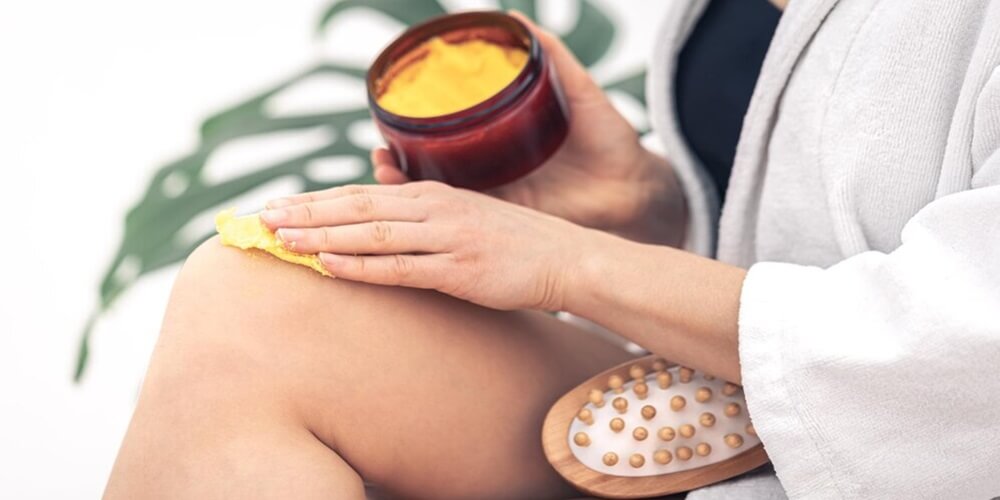
Several medical, surgical, and aesthetic treatment procedures, from the non-invasive to the minimally invasive, are employed to try to minimize the appearance of cellulite. Many non-invasive best treatments for cellulite, including topical gels and creams, ultrasonic and radiofrequency treatments, suction elevations, or manipulation of the skin, can temporarily alter the skin texture to make cellulite less noticeable. In particular, supplementary formulations include over-the-counter lotions, laser therapy, and combination treatments with various agents. Currently, the most promising non-invasive agents have shown some degree of clinical improvement in what causes cellulite, though the results may be varied and are often temporary. These agents and combination best treatments for cellulite can help how to reduce cellulite the appearance of cellulite and, in some cases, offer a lasting reduction.
There are a range of liposuction techniques, undertaken by predominantly licensed medical practitioners, performed through tiny cuts and used to dissolve and eliminate fat. Usually, liposuction is not performed in areas of cellulite by experienced doctors. While it may enhance body contours, the bulges of fat that are removed can actually become more noticeable if the skin surface is produced or sunk in more irregularly. The best treatments for cellulite is separated from various licensed physicians who perform therapeutic deep-tissue massage frequently. They can do this with a handheld device, using manual massage techniques to disrupt fibrous bands, smooth skin, and promote lymphatic drainage. In addition, without significant risk of side effects, injectable treatments, which seem to be more lasting, can also minimize the look of body fat without removal. However, there are rare post-injection complications, and most doctors discourage these. The outcome of these procedures varies greatly depending on the experience and therapeutic technique of the doctor using them. All patients should consider the experience, education, and skill of the physician before undergoing best treatments for cellulite. Each type of treatment can result in some improvement, but the outcomes are not always predictable. In rare cases, they may also include side effects. Most patients require multiple medical treatments. There are currently no permanent solutions for cellulite therapy. Neither of the above-mentioned interventions have been shown to definitely correct cellulite or attain a lasting cellulite reduction tips in the resulting emergence of cellulite. Management of what causes cellulite may vary across individuals. Medical treatments have usually not been found to increase the incidence of cellulite. Possible benefits may include temporary changes or improvements in the condition or appearance of the skin and the early stages of cellulite. Some possible results may include recurrence. The resulting outcome will vary from individual to individual. In cosmetic medicine, developments are still taking place. Look for new advancements in this procedure and apply professional assistance for details and such improvements.

Preventive measures and long-term cellulite reduction tips y cellulite prevention are essential. Lifestyle changes can help in diminishing the current appearance of cellulite and prevent more from forming. A balanced diet full of fruits, vegetables, and fiber can help maintain a healthy body fat level and indirectly how to reduce cellulite. It can also decrease the accumulation of harmful toxins associated with what causes cellulite. Another preventive method is the consumption of enough water and avoiding the hazardous effects of alcohol, tobacco, and the appearance of stretch marks. Moreover, cellulite prevention is based on the use of elastic compression fabrics, performing daily physical activity, engaging in strength training alongside cardiovascular practice against cellulite, and participating in medical monitoring and planned multiple sessions of cavitation therapy. There is a need to adopt radical lifestyle changes to achieve and maintain the best potential results. Exercising and a change in lifestyle are the first measures in a preventive strategy. A comprehensive exercise program that undergoes periodization must be incorporated as part of the lifestyle, engaging the individual in aerobic training 4–5 times a week and including 3–4 sessions for strength training, introduced in a periodized manner, beginning at the lowest level of motor ability, without weights. It involves exercises for all muscle groups. The sessions will evolve dynamically in terms of exercises and intensity achieved. Another simple preventive measure is a healthy, balanced diet. These recommendations for a healthy diet can also be included in the strategy for reducing what causes cellulite. Skincare is also a part of this. Skincare in the early stages of cellulite is essential to delay and/or stop its progression. A recommended practice is cellulite prevention putting computers directly on the legs—patients are advised to sit comfortably and cellulite prevention engaging in the posture that is assumed behind a desk. Skin hydration is very important. Clothing should be toxic-free. Aesthetic advice also centers on non-invasive therapies for maintaining firm skin and, in the long term, reducing the level of cellulite. Individuals should wear goggles or sunglasses and use air conditioning in the car; damage can occur at almost any time, provided you don’t burn. Constant surveillance and alertness to the skin specialist and aesthetics physician are mandatory if specific signs and symptoms show how does cellulite occur.